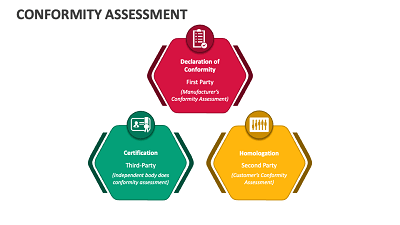
ISO/IEC 17000:2004 is a standard developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). The full title of the standard is “Conformity assessment – Vocabulary and general principles.”
This standard provides a set of terms and definitions related to conformity assessment, aiming to ensure a common understanding of the concepts and principles involved in this field. Conformity assessment is the process of demonstrating that specified requirements relating to a product, process, system, person, or body are fulfilled.
Key points covered in ISO/IEC 17000:2004 include:
- Vocabulary: The standard provides a comprehensive list of terms and definitions related to conformity assessment. This helps in avoiding ambiguity and ensuring that stakeholders have a shared understanding of the terminology used in this field.
- General Principles: ISO/IEC 17000 outlines fundamental principles that underpin conformity assessment activities. These principles include concepts such as impartiality, competence, consistency, and confidentiality, among others.
- Accreditation and Certification: The standard addresses the importance of accreditation and certification bodies in the conformity assessment process. It emphasizes the need for these bodies to operate in accordance with established principles and practices to ensure the credibility and reliability of conformity assessment results.
- Decision Rules: ISO/IEC 17000 also discusses decision rules and the factors that should be considered when determining conformity or nonconformity. This is crucial in maintaining consistency and objectivity in assessment outcomes.
- Documentation and Records: The standard highlights the significance of documentation and record-keeping in conformity assessment. Proper documentation is essential for traceability, transparency, and the ability to demonstrate conformity with specified requirements.
It’s important to note that standards are periodically reviewed and updated. As of my last knowledge update in January 2022, there might be newer versions or revisions of ISO/IEC 17000. Therefore, it’s advisable to check the latest edition of the standard for any changes or updates that may have occurred since then.
What is required ISO/IEC 17000:2004 Conformity assessment
ISO/IEC 17000:2004 provides general principles and vocabulary for conformity assessment. It doesn’t specify requirements for the specific processes involved in conformity assessment, but rather establishes a framework and common terminology for understanding and discussing conformity assessment activities. However, it lays the groundwork for the development of other standards that do specify requirements for various aspects of conformity assessment.
If an organization or entity wants to conform to the principles outlined in ISO/IEC 17000, it may consider the following key points:
- Understanding Vocabulary and Principles: The organization should familiarize itself with the vocabulary and general principles provided in ISO/IEC 17000. This involves a comprehensive understanding of the terms used in the conformity assessment field and the overarching principles such as impartiality, competence, and consistency.
- Implementing General Principles: Adopting and implementing the general principles outlined in ISO/IEC 17000 within the organization’s processes is essential. This includes ensuring impartiality, maintaining competence, and striving for consistency in conformity assessment activities.
- Compliance with Relevant Standards: ISO/IEC 17000 serves as a foundation for other standards that provide specific requirements for different aspects of conformity assessment, such as ISO/IEC 17025 for testing and calibration laboratories or ISO/IEC 17021 for certification bodies. Organizations may need to comply with these specific standards if they are engaged in particular types of conformity assessment activities.
- Documentation and Records: While ISO/IEC 17000 does not prescribe specific documentation requirements, maintaining proper documentation and records is generally a good practice. Documenting procedures, decisions, and outcomes is crucial for transparency, traceability, and the ability to demonstrate conformity with specified requirements.
- Continuous Improvement: Embracing a culture of continuous improvement is in line with ISO/IEC 17000. Organizations should regularly review their conformity assessment processes, identify areas for improvement, and implement corrective actions as needed.
It’s important to note that the specifics of conformity assessment processes will depend on the type of conformity assessment being performed (e.g., testing, certification, inspection) and the relevant standards associated with those specific activities. Organizations should refer to the appropriate standards applicable to their field for detailed requirements. Additionally, keeping up to date with the latest revisions or updates to relevant standards is essential.
Who is required ISO/IEC 17000:2004 Conformity assessment
ISO/IEC 17000:2004, titled “Conformity assessment – Vocabulary and general principles,” is a general standard that provides principles and terminology applicable to conformity assessment. It does not prescribe specific requirements for any particular sector or activity but lays down a foundation of principles and vocabulary that can be used across various conformity assessment processes.
The standard is relevant to a broad range of stakeholders involved in conformity assessment activities, including:
- Conformity Assessment Bodies (CABs): Organizations providing services related to conformity assessment, such as testing laboratories, certification bodies, inspection bodies, and calibration services, can benefit from ISO/IEC 17000. It provides a common language and general principles that can be applied across different sectors.
- Regulatory Authorities: Regulatory bodies and government agencies responsible for overseeing and regulating conformity assessment activities within specific industries or regions may reference ISO/IEC 17000 to establish a common understanding and terminology.
- Industry Associations: Associations representing specific industries or sectors may use ISO/IEC 17000 as a reference to promote consistency and understanding in conformity assessment practices among their members.
- Customers and Consumers: Organizations seeking conformity assessment services and end-users who rely on the results of conformity assessment activities can benefit from understanding the principles and terminology outlined in ISO/IEC 17000.
- Standardization Bodies: ISO/IEC 17000 is developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Standardization bodies, both at the international and national levels, may reference ISO/IEC 17000 in the development of sector-specific conformity assessment standards.
It’s important to note that ISO/IEC 17000 is a foundational document, and specific requirements for different types of conformity assessment activities are addressed in related standards. For example, ISO/IEC 17025 is specific to testing and calibration laboratories, while ISO/IEC 17021 is for certification bodies.
Organizations and individuals involved in conformity assessment processes are encouraged to consult sector-specific standards and regulations relevant to their activities in addition to ISO/IEC 17000. This ensures compliance with detailed requirements and practices specific to their field.
When is required ISO/IEC 17000:2004 Conformity assessment
ISO/IEC 17000:2004, titled “Conformity assessment – Vocabulary and general principles,” provides general principles and vocabulary applicable to conformity assessment across various sectors. It is not a standalone standard that mandates specific requirements or specifies when it is required. Instead, it serves as a foundation, offering common terminology and principles that can be applied to different conformity assessment activities.
ISO/IEC 17000 becomes relevant in the following situations:
- Development of Conformity Assessment Systems: Organizations or bodies involved in developing conformity assessment systems, procedures, or standards can refer to ISO/IEC 17000 to ensure a common understanding of terms and principles. This is particularly important when aiming for consistency and harmonization in conformity assessment practices.
- Training and Education: ISO/IEC 17000 can be used in training programs and educational materials related to conformity assessment. It helps individuals working in the field to understand key concepts and principles, fostering a common language and understanding across different stakeholders.
- Regulatory Compliance: Regulatory authorities or bodies involved in developing regulations related to conformity assessment may refer to ISO/IEC 17000 to establish a foundation for terminology and principles. While not a regulatory requirement in itself, it can provide a useful reference for developing and interpreting regulations.
- Certification Bodies and Laboratories: Conformity assessment bodies, such as certification bodies, testing laboratories, and inspection bodies, can use ISO/IEC 17000 to align their practices with recognized principles. This can enhance the credibility and consistency of their conformity assessment activities.
- Standardization Processes: ISO/IEC 17000 is a standard developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Standardization bodies may reference ISO/IEC 17000 in the development of sector-specific standards to ensure consistency and common understanding.
It’s important to note that while ISO/IEC 17000 provides a foundational framework, specific requirements for different types of conformity assessment activities are typically addressed in sector-specific standards. For example, ISO/IEC 17025 is specific to testing and calibration laboratories, while ISO/IEC 17021 is for certification bodies.
In summary, ISO/IEC 17000 is relevant in contexts where a common understanding of conformity assessment terminology and principles is needed, such as during system development, training, regulatory processes, and standardization efforts. Organizations engaged in conformity assessment activities should also refer to sector-specific standards applicable to their field.
Where is required ISO/IEC 17000:2004 Conformity assessment
ISO/IEC 17000:2004, titled “Conformity assessment – Vocabulary and general principles,” is not a mandatory standard with specific requirements that must be followed. Instead, it provides a foundation of principles and common terminology applicable to conformity assessment across various sectors.
The relevance and use of ISO/IEC 17000 can be observed in various contexts and industries, including:
- International Standardization: ISO/IEC 17000 is developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). It serves as a reference document for international standardization activities related to conformity assessment, providing a common vocabulary and general principles.
- Regulatory Frameworks: While ISO/IEC 17000 is not a legal or regulatory requirement on its own, regulatory authorities may refer to it when developing regulations or standards related to conformity assessment. It helps establish common understanding and terminology within regulatory frameworks.
- Conformity Assessment Bodies (CABs): Organizations involved in conformity assessment, such as testing laboratories, certification bodies, inspection bodies, and calibration services, may consider ISO/IEC 17000 as a guide for establishing consistent and transparent conformity assessment practices.
- Training and Education: ISO/IEC 17000 is often used in training programs and educational materials for individuals working in the field of conformity assessment. It helps impart a common understanding of key concepts and principles.
- Development of Conformity Assessment Systems: When designing or implementing conformity assessment systems or procedures, ISO/IEC 17000 can serve as a foundational document, providing principles that contribute to consistency and harmonization.
- Certification Processes: Certification bodies, in particular, may use ISO/IEC 17000 to align their practices with recognized principles, contributing to the credibility and reliability of their certification processes.
While ISO/IEC 17000 provides a common foundation, it’s important to note that specific requirements for different types of conformity assessment activities are typically addressed in sector-specific standards. For example, ISO/IEC 17025 is specific to testing and calibration laboratories, while ISO/IEC 17021 is for certification bodies.
In summary, ISO/IEC 17000 is applicable and relevant in a variety of contexts where a common understanding of conformity assessment principles and terminology is desired. Its use is voluntary, and its impact depends on how organizations and industries choose to incorporate its principles into their practices.
How is required ISO/IEC 17000:2004 Conformity assessment
ISO/IEC 17000:2004, titled “Conformity assessment – Vocabulary and general principles,” does not prescribe specific requirements or provide a certification process itself. Instead, it offers a set of principles and vocabulary to guide conformity assessment activities across various sectors. Organizations may choose to incorporate the principles outlined in ISO/IEC 17000 voluntarily, and the application of these principles can vary depending on the context and industry. Here’s how ISO/IEC 17000 might be considered or used in the context of conformity assessment:
- Adoption of Principles: Organizations engaged in conformity assessment activities, such as testing laboratories, certification bodies, inspection bodies, and calibration services, can voluntarily adopt the general principles outlined in ISO/IEC 17000. This involves understanding and applying concepts like impartiality, competence, consistency, and confidentiality in their processes.
- Training and Education: ISO/IEC 17000 is often used as a reference in training and educational programs for individuals working in the field of conformity assessment. It helps build a common understanding of key concepts and terminology, contributing to a consistent approach within the industry.
- Internal Guidance: Organizations may use ISO/IEC 17000 as internal guidance when developing or refining their conformity assessment systems. The principles and vocabulary can be referenced to ensure a clear and standardized approach to conformity assessment activities within the organization.
- Regulatory Compliance: Regulatory authorities or bodies may refer to ISO/IEC 17000 when developing regulations or standards related to conformity assessment. Although compliance with ISO/IEC 17000 is not mandatory, aligning with its principles can contribute to consistency and common understanding within regulatory frameworks.
- Integration with Sector-Specific Standards: ISO/IEC 17000 serves as a foundational document, and its principles are often integrated into more specific conformity assessment standards for different sectors. Organizations may need to comply with these sector-specific standards for certification or accreditation in their respective fields.
It’s important to note that ISO/IEC 17000 is not a certification standard, and conformity assessment bodies do not typically seek ISO/IEC 17000 certification. Instead, organizations might use it as a reference to improve the quality and credibility of their conformity assessment activities.
If an organization is seeking certification or accreditation, it would typically refer to more specific standards related to its type of conformity assessment work. For example, ISO/IEC 17025 for testing and calibration laboratories, ISO/IEC 17021 for certification bodies, or ISO/IEC 17020 for inspection bodies. These standards provide detailed requirements for the respective conformity assessment activities.
Case Study on ISO/IEC 17000:2004 Conformity assessment
While ISO/IEC 17000:2004 itself is a foundational standard that provides general principles and vocabulary for conformity assessment, it doesn’t lend itself to specific case studies since it doesn’t prescribe specific requirements or processes. However, we can create a hypothetical case study that illustrates how an organization might apply the principles outlined in ISO/IEC 17000 in the context of conformity assessment.
Hypothetical Case Study: XYZ Certification Services
Background: XYZ Certification Services is a certification body offering management system certification services to organizations in the food industry. The organization has decided to align its practices with ISO/IEC 17000 to enhance the credibility and transparency of its certification processes.
Implementation Steps:
- Understanding ISO/IEC 17000:2004:
- XYZ Certification Services begins by thoroughly studying ISO/IEC 17000 to understand the general principles and vocabulary related to conformity assessment.
- Internal Training:
- The organization conducts internal training sessions to educate its staff on the principles outlined in ISO/IEC 17000. This training helps staff members develop a common understanding of key concepts, such as impartiality, competence, and consistency.
- Documentation and Policies:
- XYZ Certification Services revises its documentation, including policies and procedures, to reflect the principles outlined in ISO/IEC 17000. This includes clearly defining terms, documenting processes, and establishing mechanisms for ensuring impartiality in certification activities.
- Stakeholder Communication:
- The organization communicates with its clients and other stakeholders about its commitment to following ISO/IEC 17000 principles. This transparency builds trust and confidence among clients and helps demonstrate the organization’s dedication to best practices in conformity assessment.
- Internal Audits:
- XYZ Certification Services incorporates ISO/IEC 17000 principles into its internal audit processes. Internal audits are conducted to assess the organization’s adherence to these principles, ensuring that its conformity assessment practices are in line with industry-recognized standards.
- Continuous Improvement:
- The organization establishes a continuous improvement process, regularly reviewing and updating its practices based on feedback, audit results, and changes in the industry. This ensures that the principles outlined in ISO/IEC 17000 are consistently applied and adapted to evolving circumstances.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Credibility: XYZ Certification Services experiences increased credibility in the market as clients recognize its commitment to following internationally recognized principles in conformity assessment.
- Client Satisfaction: Clients appreciate the transparency and consistency in certification processes, leading to improved satisfaction and long-term relationships.
- Competitive Advantage: Adhering to ISO/IEC 17000 principles provides XYZ Certification Services with a competitive advantage, as it stands out as a certification body committed to industry best practices.
Conclusion: While ISO/IEC 17000:2004 doesn’t provide a certification framework, the principles it outlines can be applied by organizations voluntarily seeking to improve their conformity assessment processes. In this hypothetical case, XYZ Certification Services aligns its practices with ISO/IEC 17000, leading to enhanced credibility, client satisfaction, and a competitive edge in the market.
White Paper on ISO/IEC 17000:2004 Conformity assessment
White Paper on ISO/IEC 17000:2004 – Conformity Assessment
Executive Summary:
ISO/IEC 17000:2004, titled “Conformity assessment – Vocabulary and general principles,” serves as a foundational document providing essential principles and a standardized vocabulary for organizations engaged in conformity assessment activities. While it does not specify requirements for particular sectors, it offers a framework for ensuring transparency, competence, and consistency in conformity assessment.
This white paper aims to provide an overview of ISO/IEC 17000, its significance, and how organizations can leverage its principles to enhance their conformity assessment practices.
Introduction:
Conformity assessment is a critical process that verifies whether a product, service, or system complies with specified requirements. ISO/IEC 17000 establishes a common language and set of principles that facilitate clear communication and understanding within the conformity assessment community.
Key Principles of ISO/IEC 17000:
- Impartiality:
- Organizations must demonstrate impartiality in their conformity assessment activities, ensuring that their decisions are not influenced by conflicting interests.
- Competence:
- Personnel involved in conformity assessment must possess the necessary competence to carry out their tasks effectively. This includes education, training, and experience.
- Consistency:
- Conformity assessment activities should be conducted consistently over time and across different instances, ensuring reliability and repeatability of results.
- Confidentiality:
- Organizations must handle information obtained during conformity assessment activities with confidentiality, protecting the interests of the assessed party.
- Transparency:
- Transparency in processes and decision-making is crucial. Stakeholders should be able to understand the methods used, criteria applied, and decisions made during conformity assessment.
Application in Practice:
Organizations involved in conformity assessment can use ISO/IEC 17000 as a guide to improving their practices. Some key steps include:
- Training and Awareness:
- Conduct training sessions to ensure all staff members understand the principles outlined in ISO/IEC 17000.
- Internal Documentation:
- Review and update internal documentation, policies, and procedures to align with the vocabulary and principles of ISO/IEC 17000.
- Stakeholder Communication:
- Communicate with clients, regulators, and other stakeholders about the organization’s commitment to ISO/IEC 17000 principles.
- Audit and Review:
- Integrate ISO/IEC 17000 principles into internal audit processes, regularly reviewing and improving conformity assessment practices.
Benefits of ISO/IEC 17000 Implementation:
- Enhanced Credibility:
- Organizations aligning with ISO/IEC 17000 principles gain credibility in the marketplace, signaling a commitment to best practices.
- Consistent Practices:
- The adoption of consistent conformity assessment practices leads to more reliable and repeatable results.
- Improved Stakeholder Confidence:
- Stakeholders, including clients and regulatory bodies, gain confidence in the organization’s ability to conduct reliable conformity assessments.
- International Recognition:
- Conforming to ISO/IEC 17000 establishes a common ground for communication and understanding globally, facilitating international recognition.
Conclusion:
ISO/IEC 17000:2004 serves as a cornerstone for conformity assessment by providing a common language and foundational principles. Organizations can benefit significantly by voluntarily aligning their practices with the principles outlined in this standard. This white paper encourages organizations to explore the application of ISO/IEC 17000, fostering a culture of transparency, competence, and consistency in conformity
Industrial Application on ISO/IEC 17000:2004 Conformity assessment
In industrial settings, the principles and vocabulary outlined in ISO/IEC 17000:2004 can be applied to various conformity assessment activities. Here’s an exploration of how ISO/IEC 17000 can be relevant in an industrial context:
1. Product Certification:
- Scenario: A manufacturing company produces electrical components. To enhance the marketability of its products, the company seeks certification according to ISO/IEC 17000 principles.
- Application:
- The company establishes transparent conformity assessment processes based on ISO/IEC 17000 principles, ensuring that the certification decisions are impartial and consistent.
- Personnel involved in the certification process are trained and assessed for competence according to ISO/IEC 17000 guidelines.
- The certification body communicates with stakeholders, including customers and regulatory bodies, to build trust and demonstrate adherence to internationally recognized conformity assessment principles.
2. Quality Management System Audits:
- Scenario: An industrial facility implements a quality management system (QMS) and seeks conformity assessment through internal and external audits.
- Application:
- Internal auditors use ISO/IEC 17000 as a reference to ensure consistency in auditing processes and decision-making.
- The organization communicates its commitment to ISO/IEC 17000 principles to external auditors, fostering confidence in the reliability of the QMS.
- The organization maintains a transparent and documented audit trail, incorporating ISO/IEC 17000 vocabulary to facilitate understanding and traceability.
3. Supplier Audits:
- Scenario: An automotive manufacturer conducts conformity assessments of its suppliers to ensure the quality of incoming components.
- Application:
- The automotive manufacturer aligns its supplier audit processes with ISO/IEC 17000 principles to maintain consistency across various suppliers.
- Auditors demonstrate impartiality by avoiding conflicts of interest and ensuring that assessment decisions are solely based on objective evidence.
- The manufacturer communicates its adherence to ISO/IEC 17000 principles to suppliers, promoting transparency and encouraging similar principles in their operations.
4. Environmental Impact Assessment:
- Scenario: An industrial facility undergoes an environmental impact assessment for regulatory compliance.
- Application:
- The assessment process follows ISO/IEC 17000 principles to ensure impartiality and consistency in evaluating the environmental impact.
- Personnel involved in the assessment, including environmental consultants, adhere to competency requirements outlined in ISO/IEC 17000.
- The assessment report uses standardized vocabulary from ISO/IEC 17000, facilitating communication with regulatory bodies and stakeholders.
5. Accreditation of Testing Laboratories:
- Scenario: An industrial testing laboratory seeks accreditation for its services.
- Application:
- The laboratory aligns its quality management and testing processes with ISO/IEC 17000 principles.
- During the accreditation process, the laboratory demonstrates competence of its personnel according to ISO/IEC 17000 guidelines.
- The laboratory communicates its commitment to ISO/IEC 17000 principles to clients, promoting confidence in the reliability of test results.
Conclusion:
In industrial applications, ISO/IEC 17000 provides a valuable framework for conformity assessment, promoting transparency, competence, and consistency. Whether applied to product certification, quality management system audits, supplier assessments, environmental impact evaluations, or laboratory accreditations, ISO/IEC 17000 principles contribute to building trust, improving reliability, and ensuring the effectiveness of conformity assessment activities in industrial settings.